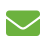
Hallgrímskirkja
The Hallgrímskirkja (Icelandic pronunciation: [?hatlkrims?c??rca], church of Hallgrímur) is a Lutheran (Church of Iceland) parish church in Reykjavík, Iceland. At 74.5 metres (244 ft), it is the largest church in Iceland and the sixth tallest architectural structure in Iceland after Longwave radio mast Hellissandur, the radio masts of US Navy at Grindavík, Eiðar longwave transmitter and Smáratorg tower. The church is named after the Icelandic poet and clergyman Hallgrímur Pétursson (1614 to 1674), author of the Passion Hymns.
State Architect Guðjón Samúelsson's design of the church was commissioned in 1937. He is said to have designed it to resemble the basalt lava flows of Iceland's landscape. It took 38 years to build the church. Construction work began in 1945 and ended in 1986, the landmark tower being completed long before the church's actual completion. The crypt beneath the choir was consecrated in 1948, the steeple and wings were completed in 1974. The nave was consecrated in 1986.[1] Situated in the centre of Reykjavík, it is one of the city's best-known landmarks and is visible throughout the city. It is similar in style to the expressionist architecture of Grundtvig's Church of Copenhagen, Denmark, completed in 1926.
The church houses a large pipe organ by the German organ builder Johannes Klais of Bonn. It has mechanical action, four manuals and pedal, 102 ranks, 72 stops and 5275 pipes. It is 15 metres tall and weighs 25 tons. Its construction was finished in December 1992. It has been recorded by Christopher Herrick in his Organ Fireworks VII CD.
The church is also used as an observation tower. An observer can take a lift up to the viewing deck and view Reykjavík and the surrounding mountains. The statue of explorer Leif Eriksson (1929-32) by Alexander Stirling Calder in front of the church predates its construction. It was a gift from the United States in honor of the 1930 Alþingi Millennial Festival, commemorating the 1000th anniversary of Iceland's parliament at Þingvellir in 930 AD.
In 2008, the church underwent a major restoration of the main tower, and was covered in scaffolding. In late 2009, restoration was completed and the scaffolding was removed.

Comments
Sign in or get an account to comment.