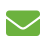
Désespoir des singes
Araucaria araucana (commonly called the monkey puzzle tree, monkey tail tree, Chilean pine, or pehuén) is an evergreen tree growing to 40 metres (130 ft) tall with a 2 metres (7 ft) trunk diameter. The tree is native to central and southern Chile and western Argentina.[1] Araucaria araucana is the hardiest species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Because of the great age of this species it is sometimes described as a living fossil. It is the national tree of Chile.
Araucaria araucana is a popular garden tree, planted for its unusual effect of the thick, 'reptilian' branches with a very symmetrical appearance. It prefers temperate climates with abundant rainfall, tolerating temperatures down to about ?20 °C (?4 °F). It is far and away the hardiest member of its genus, and can grow well in western Europe (north to the Faroe Islands and Smøla[3] in western Norway), the west coast of North America (north to the islands of Haida Gwaii in Canada) and locally on the east coast as well, and in New Zealand and southeastern Australia. It is tolerant of coastal salt spray, but does not like exposure to pollution.
Its seeds are edible, similar to large pine nuts, and are extensively harvested in Chile. The tree has some potential to be a food crop in other areas in the future, thriving in climates with cool oceanic summers (e.g. western Scotland) where other nut crops do not grow well. A group of six female trees with one male for pollination could yield several thousand seeds per year. Since the cones drop, harvesting is easy. The tree however does not yield seeds until it is around 30-40 years old, which discourages investment in planting orchards (although yields at maturity can be immense); once established, it can live possibly as long as 1,000 years (Gymnosperm Database). Once valued because of its long, straight trunk, its current rarity and vulnerable status mean its wood is now rarely used; it is also sacred to some members of the Mapuche Native American tribe.[4] Before the tree became protected by law in 1971, there were lumber-mills in Araucanía Region which specialized in Araucarias. This species is listed in the CITES Appendix I as an endangered species.
First found in Chile in the 1780s, it was named Pinus araucana by Molina in 1782. In 1789, de Jussieu had erected a new genus called Araucaria based on the species, and in 1797 Pavón published a new description of the species which he called Araucaria imbricata (an invalid name, as it did not use Molina's older species epithet). Finally, in 1873, after several further redescriptions, Koch published the combination Araucaria araucana, validating Molina's name in the genus. The name araucana is derived from the native Araucanians who used the nuts (seeds) of the tree in Chile. A group of Araucanians living in the Andes, the Pehuenches, owe their name to their diet based on harvesting of the Araucaria seeds. Pehuen means Araucaria and che people in Mapudungun. The origin of the popular English language name monkey puzzle derives from its early cultivation in Britain in about 1850, when the species was still very rare in gardens and not widely known. The proud owner of a young specimen at Pencarrow garden near Bodmin in Cornwall was showing it to a group of friends, and one made the remark "It would puzzle a monkey to climb that"; as the species had no existing popular name, first 'monkey puzzler', then 'monkey puzzle' stuck. In France, it is known as désespoir des singes or 'monkeys' despair'.
This will be my Monthly Blip Challenge entry for the theme of Nature

Comments
Sign in or get an account to comment.